The vermilion, amethyst and jade ribbons of the northern and southern lights are some of Earth’s most distinctive features. But our planet has no monopoly on auroras. Scientists have spied them throughout the solar system, weaving through the skies of Mars, Saturn, Jupiter and even on some of Jupiter’s fiery and icy moons.
Lights glow in the skies of Uranus, too. But auroras around our sun’s most distant planet, Neptune, have long eluded astronomers.
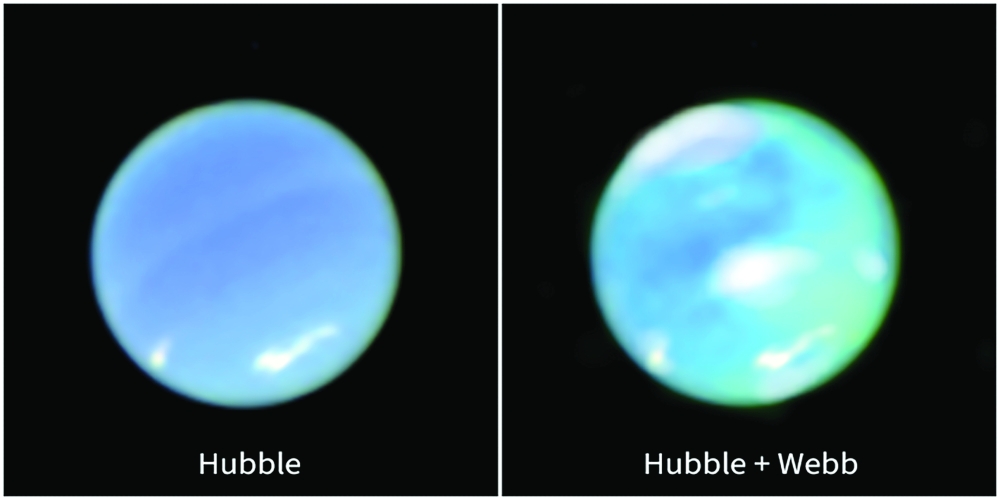
That has changed with the powerful infrared instruments aboard the James Webb Space Telescope. In a study in the journal Nature Astronomy, scientists reveal unique auroras that spill over either side of Neptune’s equator, a contrast with the glowing gossamer seen arcing over other worlds’ poles.
Astronomers are thrilled to see the completion of an aurora-hunting quest decades in the making. “Everyone is very excited to prove that it’s there, just like we thought,” said Rosie Johnson, a space physics researcher at Aberystwyth University in Wales who wasn’t involved with the new study.
This discovery will also allow scientists to study aspects of Neptune that have previously been out of reach. “They’re using aurora to understand the shape of the planet’s magnetic field, which is seeing the unseen,” said Carl Schmidt, a planetary astronomer at Boston University who wasn’t involved with the new study.
Each world generates auroras differently, but the basics are the same. Energetic particles slam into an atmosphere and bounce off gases. That particle collision briefly causes flashes of light. And if a world has a magnetic field, that guides the location of the auroras.
Auroras don’t always glow in visible light; Saturn, for example, emits mostly ultraviolet auroras. But they can be observed with the right telescopes. It hasn’t been possible until now to spot Neptune’s atmospheric lights. “Astronomers have been trying to detect the aurora of Neptune for decades, and each attempt has failed,” said Henrik Melin, a planetary scientist at Northumbria University in England and one of the study’s authors. — ROBIN GEORGE ANDREWS / NYT
Oman Observer is now on the WhatsApp channel. Click here